last edited for clarity 11:05 CDT 3/14/2012
A recent article by S. Fred Singer in American Thinker entitled Climate Deniers are Giving Us Skeptics a Bad Name has caused a resurgence of attacks against those of us who believe that the Earth does indeed have a “greenhouse effect” which makes the Earth’s surface warmer than it would otherwise be.
As a result of Fred’s article, angry E-mails have been flying like arrows, and belligerent blog posts have littered the landscape. (Well, maybe that’s a bit of an exaggeration. But I enjoyed writing it.)
In the American Thinker article, Fred has taken the tack that the “denier” label (which left-leaning folk seem to love calling us) should be applied to those who deny the so-called greenhouse effect (which states that infrared absorbing gases in the atmosphere perform a surface-warming function) and should not be applied to those of us who are skeptical of how much humans have warmed the climate system by slightly enhancing the natural greenhouse effect with more carbon dioxide from burning of carbon based fuels. The anti-greenhouse crowd’s bible seems to be the book, Slaying the Sky Dragon – Death of the Greenhouse Gas Theory.
The arguments between us and the anti-greenhouse advocates often become technical and devolve into disputes over the 1st or 2nd Law of Thermodynamics, whether photons really exist, whether a carbon dioxide molecule which absorbs IR energy immediately releases it again, whether outer space is an ‘insulator’, etc. Lay people quickly become overwhelmed, and even some of us technical types end up feeling ill-equipped to argue outside our areas of expertise.
I believe the fact that infrared-absorbing gases warm the surface and lower atmosphere can be easily demonstrated with 2 simple steps. The first step is in the realm of everyone’s daily experience. The second step is based upon satellite measurements of the Earth giving off infrared energy, measurements which were first made over 40 years ago.
The Alabama Two-Step
STEP 1:
Temperature is determined by rates of energy gain and energy loss. It does not matter whether we are talking about the human body, a car engine, a pot of water on the stove, or the climate system. The temperature (and whether it is rising or falling) is determined by the rates of energy gain and energy loss. In the case of the climate system, the Earth receives energy from the sun (primarily at visible wavelengths of light), and loses energy to outer space (primarily at infrared wavelengths). A temperature rise can occur either from (1) increasing the rate of energy gain, or (2) decreasing the rate of energy loss. The greenhouse effect has to do with the 2nd of these possibilities.
STEP 2:
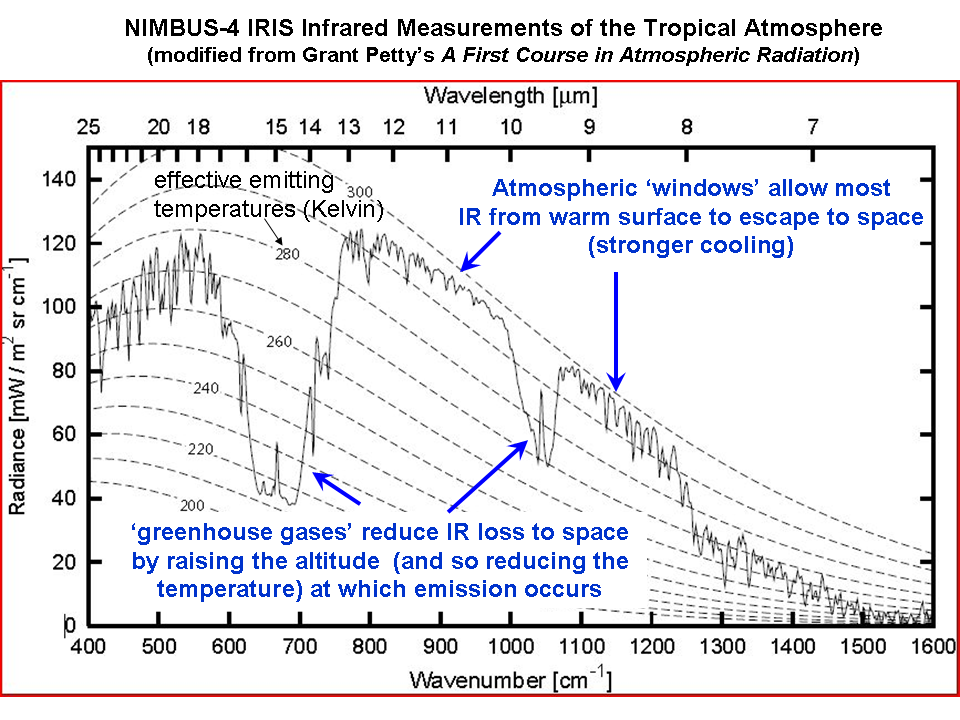
Infrared absorbing gases reduce the rate at which the Earth loses infrared energy to space. Satellite measurements of the rate at which the Earth loses infrared energy to space have been made as early as the 1970’s, from the NASA Nimbus 4 spacecraft. The following plot shows the IR intensity (vertical axis) as a function of IR wavelength (horizontal axis). The area under the jagged curve is proportional to the rate of energy loss to space. Note that at the wavelengths where water vapor, carbon dioxide, and ozone absorb and emit IR energy, the rate of energy loss by the Earth is reduced.
Now, lets take Steps 1 and 2 together: If you add more of these “greenhouse gases” and nothing else changes then the rate at which the Earth, as a whole, loses energy to space is reduced. This must lead to a warming tendency, at least at the surface and lower atmosphere (the upper atmosphere will actually experience a cooling effect).
If your head is already exploding at this point, let’s use the (admittedly imperfect) analogy of a thermal IR image of a house at night, which shows how the windows and poorly insulated parts of a house are points of greater IR energy loss:
When you add insulation to your house, you reduce the rate of energy loss in the winter, which will raise the temperature inside the house (all other things being the same), while at the same time reducing the temperature of the exterior of the house. Similarly, greenhouse gases provide “radiative insulation” to the climate system, raising the temperature of the surface and lower atmosphere, while lowering the temperature of the middle and upper atmosphere.
The above analysis is, I believe, consistent with the views of MIT’s Dick Lindzen. It clearly demonstrates that IR absorbing gases (greenhouse gases) reduce the Earth’s ability to cool to outer space. No amount of obfuscation or strawman arguments in the comments section, below, will be able to get around this fact.
But HOW MUCH Warming?
The question of how much warming will result from adding carbon dioxide to the atmosphere is what we skeptics are skeptical of. The climate system is amazingly complex, and the IPCC position that elements within the climate system (especially clouds) will change in ways which amplify the resulting small warming tendency is highly questionable, to say the least. If the climate system instead acts to reduce the warming, then anthropogenic global warming (AGW) becomes for all practical purposes a non-issue.
This represents what I believe to be the simplest description of how greenhouse gases cause warming of the surface. It bypasses all of the esoteric discussions and instead deals only with observations, which I believe cannot be easily explained any other way:
FIRST, warming can be caused by a decrease in the rate of energy loss by the climate system (or any other system, for that matter).
SECOND, IR absorbing gases are observed from satellites to reduce the rate of energy loss to space.
THEREFORE, adding more IR absorbing gases will cause a warming tendency.
QED.
Again I emphasize, however, the above simple argument is necessarily true only to the extent that all other elements of the climate system remain the same, which they will not. These other changes are called ‘feedbacks’, and they can either make or break theories of global warming and associated climate change.
Regarding the Inevitable Questions…
1. Yes, the CO2 absorption bands are already mostly saturated…but the wings of those bands are not, as is evident in the above graph of satellite measurements. This saturation effect partly explains why the approximate 40% increase in atmospheric CO2 since pre-industrial times has resulted in only a 1% decrease in the rate of IR loss by the Earth to space (theoretically calculated). This is already accounted for in the climate models used by the IPCC.
2. Yes, convection is indeed a major mechanism of heat loss from the Earth’s surface. It greatly reduces the surface temperature of the Earth (and, by energy conservation, greatly increases the temperature of the middle and upper troposphere). And my view is that convective effects are what will cause feedbacks to minimize surface warming from CO2 increases. Climate models already contain convection…if they didn’t the modeled surface temperature of the Earth would average around 140 deg. F.
The global warming narrative advanced by the IPCC involves a chain of physical processes which must all be true in order for their conclusions to be true. The existence of the greenhouse effect is, in my view, one of the stronger links in the chain. Feedbacks are the weakest link.

 Home/Blog
Home/Blog